Glucosamine is a natural chemical compound found in the body. As a supplement, glucosamine is most often used to try to ease the joint pain caused by arthritis.
Why do people take glucosamine?
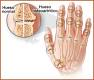
Glucosamine helps keep the cartilage in joints healthy. But natural glucosamine levels drop as people age. This can lead to gradual deterioration of the joint.
There's some evidence that glucosamine sulfate supplements help counteract this effect, although experts aren’t sure exactly how they work. Specifically, glucosamine has been shown in some studies to help ease the pain of mild to moderate osteoarthritis of the knee. Glucosamine may also help with other joint pain caused by osteoarthritis.
Glucosamine has also been used to try and treat rheumatoid arthritis and other conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease, asthma, allergies, chronic venous insufficiency, sports injuries, temporomandibular joint problems (TMJ), chronic low back pain, and many others. So far, these uses of glucosamine are not well supported by evidence from research studies.
How much glucosamine should you take?
For osteoarthritis, the typical dose of glucosamine used in most studies was 500 milligrams of glucosamine sulfate taken three times a day. Ask your doctor about specific dosing. Some experts recommend taking glucosamine with meals to prevent stomach upset.
Can you get glucosamine naturally from foods?
Although glucosamine sulfate supplements are often manufactured from the outer shells of shellfish, there aren't any natural food sources of glucosamine.
What are the risks of taking glucosamine?
- Side effects from glucosamine are generally mild.Studies have found that the side effects from standard doses of glucosamine aren't different from those of a placebo. At higher doses, side effects may be more likely. Side effects include upset stomach, heartburn, drowsiness, and headache. The level of glucosamine that would cause an overdose is unknown. On the whole, glucosamine seems to be a fairly safe supplement.
- Risks. People with allergies to shellfish should be wary of using glucosamine, since it could cause an allergic reaction. Those who have diabetes, kidney disease, heart disease, bleeding disorders, or high blood pressure should check with a doctor before using glucosamine.
- Interactions. People taking other medicines including heart medicines, insulin, blood thinners, and diuretics should check with their doctors before taking glucosamine.
Given the lack of evidence about its safety, glucosamine is not recommended for children or for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
The most common type of glucosamine supplement on the market is glucosamine sulfate. See the links below for in-depth information on glucosamine sulfate.
Glucosamine is a dietary supplement distributed as a salt; commonly, but not limited to, glucosamine HCl, glucosamine sulfate potassium, and glucosamine sulfate sodium. More common now is Glucosamine and Chondroitin, coupled with anti-oxidants.
Glucosamine aids in the formation of connective tissue including collagen and cartilage; consisting of glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) & proteoglycans. It is an effective supplement which is made more powerful when consumed with Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM).
Current research shows it may play a role in relieving arthritis.



.jpg)

.jpg)



No comments:
Post a Comment